A customer Data Platform (CDP) can be a powerful tool in the Marketing arsenal of any business that has a digital presence. In today’s day and age every business is digital (almost). What makes CDP great is the wide variety of use cases that it can support for Marketeers and unifying all the information from various other software to give a 360-degree view of customers, consumers, visitors, and users.
Marketers historically used systems built or deployed by IT (e.g., CRM systems and data warehouses). As the demand for resources from IT grew, marketers tried to go it alone. They looked to their martech stacks — often campaign management tools — to manage customer data and produce marketing insights. But this situation grew increasingly difficult. Over time, marketing and IT systems failed to keep pace with the number of channels and data sources marketers required. They also failed to enable real-time data management and customer experiences. Marketers caught between limited capabilities and aging technology turned to an emerging category, the CDP, to close the gap.
Even now CDP may not be the right fit for all. To understand if CDP is right for you look at this decision tree by Gartner that shows how and where the CDP can be helpful.
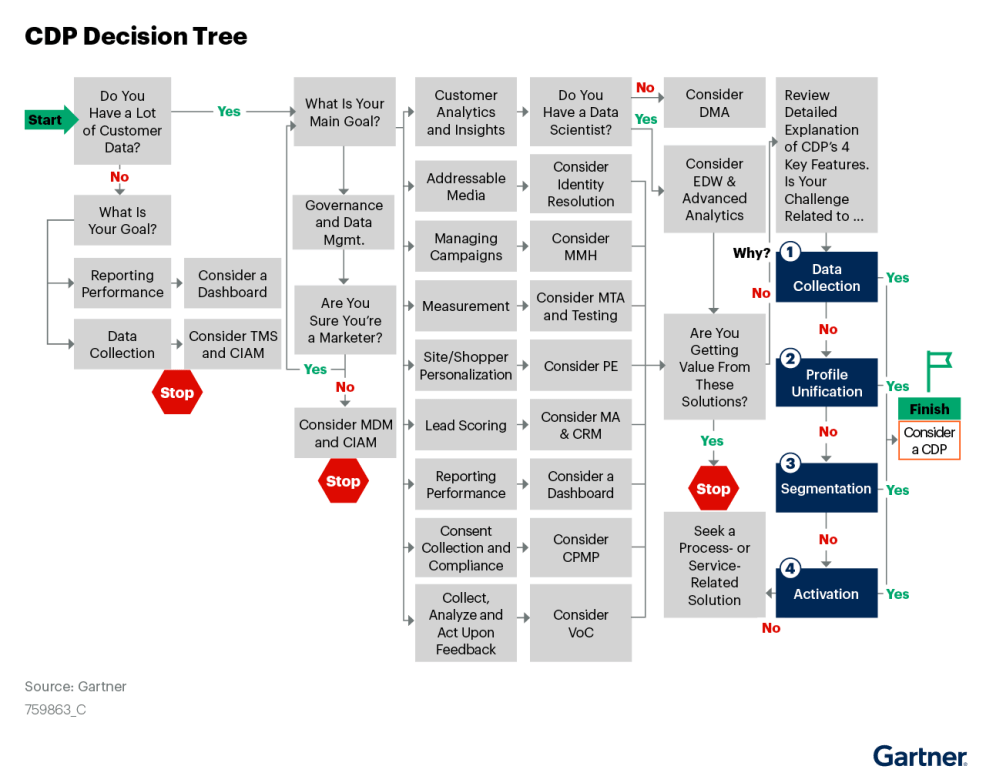
If the conclusion of your decisioning turns into the need for a Customer Data Platform use the following to plan ahead.
- It’s predicted that 70% of CDP vendors will be acquired by larger CDP vendors over the next few years. The Future of Commerce
- By 2026, 80% of organizations pursuing a 360-degree view of the customer will abandon it because it doesn’t adhere to data privacy regulations, relies on obsolete data collection methods and obliterates customer trust. Gartner
- There is a lot of overlap between CDP and related technologies such as Data Warehouse, Marketing Hub, Identity Resolution, Personalization Engines, etc. So evaluate the existing tech platforms and review before investing in CDP’s.
Core Features of a Customer Data Platform
A CDP is the core platform that can be crucial for marketing teams to have a single source of truth about their customers. The four main features of a CDP are:
- Gathering Data – The core ability to ingest and store data from various first and third party sources wether online or offline and in real time or otherwise.
- Profiling Customers (Combining Data) – The ability to consolidate profiles at the person level and connect attributes to identities.
- Profile Segmentation – The ability to provide marketeers the ability to create segments based on any and all data associated wit customer profiles.
- Data Activation – The ability to send segments and associated data with instructions to engagement tools such as email marketing, advertising, etc.
Types of Customer Data Platform
The core of any CDP is to unify customer data from multiple sources and platform, however there can be different variations of each.
- CDP Toolkits – Often custom built solutions that are needed to cater to specific needs of a business that a generic solution cannot provide. These CDP’s are ideal for IT-led teams.
- Data Aggregators – Data operations and transformation is primary use case for these CDP’s
- Smart Hub – Marketing orchestration and Personalization is the primary use case of this kind of CDP. These are the most popular solutions today since these can provide both decisioning and personalization capabilities in addition to the core CDP features.
- Marketing Cloud – These big platforms are great at capturing data. They allow marketing teams and entire enterprises to work off of a single database. Usually these platforms are available as an extension of existing enterprise softwares.

